
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has been a focal point of technological and economic discussions, with companies investing billions into AI infrastructure. The recent emergence of DeepSeek, a Chinese AI startup offering a low-cost, high-performance open-source large language model (LLM), has sent shockwaves through the market. The company’s breakthrough caused nearly $1 trillion in market cap losses for major U.S. tech companies on January 27, sparking debates about AI’s cost efficiency, investment sustainability, and long-term economic impact.
Though some view this evolution as a threat to the enormous capital expenditures (CapEx) of AI behemoths, others contend that it, in fact, legitimizes AI investment by rendering the technology more cost-effective and accessible. This piece examines the repercussions of AI cost-effectiveness, enterprise uptake, CapEx patterns, infrastructure limitations, and the overall economic revolution catalyzed by AI innovation (Reuters).
Market Disruptions & AI Cost Efficiency
DeepSeek’s AI models have highlighted the stark contrast between traditional AI infrastructure costs and new, efficient alternatives. Major U.S. tech firms have collectively invested hundreds of billions in AI-related CapEx, primarily in GPU-driven computing power. However, the availability of lower-cost AI models raises the question of whether such expenditures will continue at the same pace.
Historically, technological disruptions that improve efficiency tend to drive greater adoption rather than reduce overall investment. The computing boom of the 1990s saw firms reinvesting savings into more affordable computing capital, which fueled economic expansion. Similarly, AI’s increasing affordability could stimulate broader enterprise and consumer adoption, reinforcing the technology’s long-term trajectory.
AI Adoption & Enterprise Impact
Decreased AI prices can open up a broader variety of use cases throughout industries. Aside from the automation of mundane tasks, AI use is being extended to industries like:
Legal Support – Legal tools powered by AI can automate research, document creation, and compliance tracking.
Financial Services – AI algorithms are improving fraud detection, risk analysis, and automated trading models.
Scientific Research – Scientists are using AI for drug discovery, climate modeling, and complicated simulations.
Conversational AI – Virtual assistants and chatbots are increasingly sophisticated, managing complex interactions across enterprise operations and customer service.
As AI becomes more accessible, organizations will continue to incorporate AI-powered tools to amplify productivity and innovation, leading to pervasive digital transformation.
Decreasing AI prices can significantly impact key industries resulting in wider adoption in legal support, faster transaction processing in financial services, accelerated discoveries in scientific research, more affordable diagnostics in healthcare, higher quality interactions and more efficient AI training.
CapEx Considerations & Investment Trends
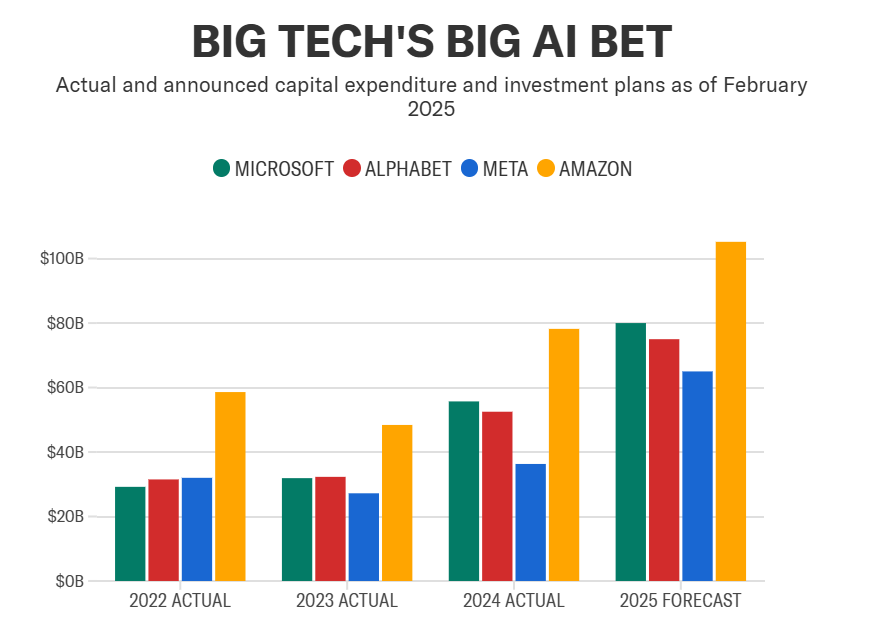
In spite of DeepSeek’s efficiency advance, experts think that AI-driven CapEx will continue to be a top concern for large tech companies. As it can be observed from the above table, demand for AI infrastructure still expands, legitimizing ongoing investment in data centers, GPUs, and AI model streamlining. Nevertheless, a transition to more power-efficient models could change spending patterns (Yahoo Finance).
The emergence of DeepSeek’s cost-effective AI models has sparked debate over whether the massive capital expenditures (CapEx) in AI infrastructure—particularly data centers—are justified. Given that AI efficiency is improving and per-token costs are declining, some argue that a linear expansion in AI adoption may not require an equivalent surge in data center investment. However, the full picture is more nuanced.
The DeepSeek event reinforces the argument that AI efficiency gains will likely reshape, but not eliminate, the need for data center investment. Companies may reassess spending trajectories, shifting from indiscriminate expansion to more optimized AI infrastructure strategies. However, given AI’s increasing adoption, data center investment will remain crucial—albeit more targeted and efficiency-driven than before.
Power & Data: The Key Constraints
With AI progressing, two basic limitations arise: power consumption and availability of data.
Energy Demands – AI data centers consume enormous amounts of power, leading to questions of sustainability. Corporations and governments are looking at solutions like low-power chips, alternative cooling methods, and renewable energy sources to mitigate these issues. With AI requiring massive energy consumption, the power sector is poised for significant investment opportunities, particularly in renewables, grid infrastructure, and energy storage.
Data Scarcity – Quality training data continues to be a bottleneck, with data privacy, availability, and biases being a concern. The emergence of synthetic data and new data marketplaces can alleviate these issues by creating realistic datasets to train AI models (KKR). Despite debates on whether massive data center expansion is necessary, the demand for data storage, processing, and networking remains high. Companies in cloud computing, semiconductor manufacturing, and data center infrastructure may offer strong investment returns.
Global AI Governance & the Paris Summit
AI’s rapid development is also putting governance and regulation in the spotlight. The Artificial Intelligence Action Summit, held on February 10-11, 2025, in Paris, France, brought together heads of state, industry leaders, and experts to discuss AI’s future. The summit saw significant investment commitments, including France’s commitment to invest €109 billion to move AI projects forward.
But the event also exposed geopolitical fault lines. The United States and United Kingdom declined to sign a declaration on “inclusive and sustainable” AI, out of fear that overregulation would stifle innovation. The move underscored global divergence on how to weigh AI development against ethical issues. While some nations are pushing for stronger AI governance, others are prioritizing economic competition and technological leadership.
Economic & Investment Outlook
Though DeepSeek may have caused some initial market shock, the economic prospects for AI in the long term continue to be favorable. Efficiency gains tend to create more competition and faster adoption, strengthening confidence in AI’s potential to transform.
Jevons Paradox & AI Demand – As AI becomes more cost-efficient, demand will increase instead of decreasing. Businesses will implement AI in new domains, widening its influence throughout industries.
AI Infrastructure & Security Expansion – Companies in AI infrastructure, tooling, and security are growing quickly, following previous technology revolutions like cloud computing and mobile technology.
AI-Driven M&A & Investments – AI startup investments, mergers, and acquisitions are on the rise as organizations look to leverage AI-driven efficiencies.
AI companies today must spend aggressively on infrastructure to ensure future growth. However, this spending will transition into sustainable revenue models as AI adoption scales, leading to strong long-term investment returns.
For investors, this means short-term volatility but potentially massive long-term gains as AI becomes a core profit driver across industries.
USA’s AI Leadership and Global Landscape
While AI’s rapid evolution raises questions of infrastructure, sustainability, and investment returns, the overall direction shows that AI will continue to revolutionize industries. The decreasing cost of AI models supports its adoption curve, ensuring innovation outpaces economic progress.
The Stargate Project is an important step in locking in America’s AI leadership, and the world’s investment in AI, such as France’s €109 billion investment, demonstrates the competitive rush for AI leadership. Regulatory talks at the Paris summit, however, show that the issue of AI’s future regulation is still open.
Despite short-term volatility in the stock market, AI’s impact on business, productivity, and economic growth is only expected to increase in the years to come.
Conclusion
The AI revolution is already entering a new phase—one where cost efficiency is facilitating greater accessibility and investment, not lessening AI’s economic viability. While DeepSeek’s advancement did rattle markets initially, it ultimately makes the case for AI-driven transformation even stronger. The Stargate Project, increasing enterprise uptake, and global AI investments all point to a future where AI will remain the driver of economic growth and technological progress.
The next ten years will be marked not by AI’s limitations but by its increasing role in reshaping industries, economies, and global power dynamics.
Work Cited
Stargate Project
https://openai.com/index/announcing-the-stargate-project/
Capital Expenditure on AI
DeepSeek sparks AI stock selloff
https://www.reuters.com/technology/chinas-deepseek-sets-off-ai-market-rout-2025-01-27/
Data & Power Problem
https://www.kkr.com/insights/2025-infrastructure-outlook
Investment and Economic Outlook 2025: AI
